WHAT IS GOLD?
Gold is a precious metal prized by humans throughout history due to its lustrous appearance and scarcity. It has been used widely throughout history in jewelers and as money and has recently found applications in electronics, medicine, and even gourmet cuisine.
Gold's combination of physical properties, rarity, historical significance, and industrial uses has contributed to its enduring value and widespread appeal across different sectors of human activity.
What is gold trading?
Gold trading refers to the buying and selling of gold as a financial asset in various markets, including commodity exchanges, futures markets, and over-the-counter (OTC) platforms. Gold is a precious metal that has been used as a store of value and a medium of exchange for centuries, making it a popular asset for investors and traders.
There are a number of reasons why you might decide to trade gold, including pure speculation, wanting to buy and take ownership of the physical gold, or as a hedge against instability.
The gold ticker symbol is XAU. The letter "X" stands for "Index," whereas the letter "AU" stands for "Aurum," the Latin word for gold.
The most popular currencies to trade against gold CFDs are the USD, AUD, CHF, EUR, and GBP. The symbol for a gold trade against the US dollar is ‘XAUUSD’, while the symbol for trading gold futures CFDs is ‘GOLD.fs’
What are factors influencing gold price?
Supply and Demand: Like any commodity, the supply and demand dynamics play a significant role in determining the price of gold. Factors such as mine production, recycling rates, central bank sales, and consumer demand for jewelry, electronics, and industrial uses can impact the supply-demand balance.
Inflation and Deflation: Gold is often seen as a hedge against inflation, as its value tends to rise when inflation rates are high. Conversely, during deflationary periods, when the purchasing power of currency increases, gold prices may experience downward pressure.
Interest Rates and Monetary Policy: Central bank policies, particularly changes in interest rates and monetary stimulus measures like quantitative easing, can influence gold prices. Lower interest rates and expansionary monetary policies generally support higher gold prices, as they reduce the opportunity cost of holding non-yielding assets like gold.
Currency Strength: Gold prices are inversely correlated with the strength of major currencies, especially the US dollar. A weaker dollar tends to make gold more attractive to investors holding other currencies, leading to higher demand and prices for gold.
Geopolitical Events and Risk Sentiment: Geopolitical tensions, conflicts, trade disputes, and political instability can drive investors towards safe-haven assets like gold, causing prices to rise. Conversely, improved geopolitical conditions and reduced risk aversion can lead to lower gold prices.
Market Sentiment and Speculation: Investor sentiment, market speculation, and trading activity in gold futures and options markets can cause short-term fluctuations in gold prices. Bullish or bearish sentiment, driven by economic data, news events, or technical analysis, can influence trader behavior and price movements.
What are top gold exchanges market?
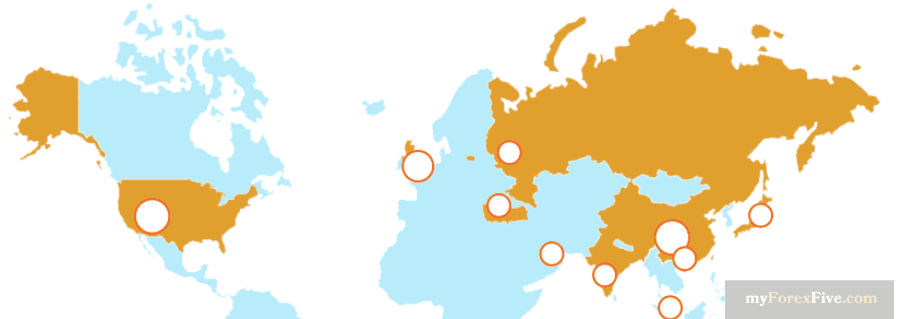
London Bullion Market Association (LBMA): is not a traditional exchange but rather an over-the-counter (OTC) market where major bullion banks and dealers trade gold and other precious metals. The LBMA sets standards for the quality and purity of gold bars (London Good Delivery bars) and facilitates trading through its member banks and participants.
Shanghai Gold Exchange (SGE): is one of the largest physical gold exchanges in the world, based in Shanghai, China. It provides a platform for trading physical gold, spot contracts, futures contracts, and options. The SGE plays a significant role in the global gold market, particularly in Asia.
COMEX (Commodity Exchange, Inc.): a division of the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) Group, is one of the largest and most influential gold futures and options exchanges in the world. It provides a platform for trading standardized gold contracts, including futures contracts with various delivery months.
Dubai Gold and Commodities Exchange (DGCX): It is located in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, offers gold futures contracts along with other commodities. It caters to traders and investors in the Middle East and provides a platform for hedging and speculation.
Multi Commodity Exchange (MCX): It is based in India, is a prominent commodity exchange where gold futures contracts are actively traded. India is one of the largest consumers of gold globally, and the MCX serves as a key platform for gold trading in the country.
New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX): Is part of the CME Group, offers gold futures contracts alongside other commodities. It is a major hub for commodity trading and attracts participants from around the world.
Tokyo Commodity Exchange (TOCOM): It is based in Japan, facilitates the trading of gold futures contracts and other commodities. It serves as an important market for gold trading in the Asia-Pacific region.
What are ways to trade gold?
Gold Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): Gold ETFs are investment funds that hold physical gold bullion as their underlying asset. Investors can buy and sell shares of these ETFs on stock exchanges, providing a convenient way to gain exposure to the gold market without dealing with physical delivery or storage of the metal.
Gold CFDs (Contracts for Difference): CFDs are financial instruments that allow traders to speculate on the price movements of gold without owning the underlying asset. With CFDs, traders can profit from both rising and falling gold prices by entering into contracts with a broker.
It is important to note that the profit or loss is determined based on the whole size of the trade position, so profits and losses are amplified.
Physical Gold: This involves buying and selling physical gold bars, coins, or jewelry. Physical gold can be purchased from bullion dealers, banks, or online platforms. It is often held as a long-term investment or used as a hedge against inflation and economic uncertainty.
Gold Futures and Options: Futures contracts and options are derivatives that allow traders to speculate on the future price movements of gold without actually owning the physical metal. Gold futures contracts are standardized agreements to buy or sell a specified amount of gold at a predetermined price on a future date. Options give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell gold at a specified price within a certain timeframe.
Gold Mining Stocks: Investing in gold mining companies' stocks is another way to gain exposure to the gold market. These stocks are influenced by factors such as gold prices, production costs, reserve estimates, and company-specific factors.
What is the best time to trade gold?

The best times to trade gold can vary depending on several factors, including market liquidity, volatility, and global economic events. Here are some key periods when gold trading activity tends to be higher and more active:
- Overlapping Trading Sessions
The most active trading times for gold often occur during the overlapping sessions of major financial markets. This includes the overlap between the London and New York trading sessions, which typically occurs from around 8:00 am to 12:00 pm (Eastern Time) when both European and North American markets are open.
- London Bullion Market Association (LBMA) Fixings
The LBMA Gold Price, which is set twice daily (morning and afternoon) through LBMA Gold Price Fixings, can create increased trading activity and price volatility around these fixing times. The morning fixing occurs around 10:30 am (London time), while the afternoon fixing occurs around 3:00 pm (London time).
- Major Economic Releases and Events
Significant economic data releases, central bank announcements, geopolitical events, and market-moving news can impact gold prices and increase trading activity. Examples include non-farm payrolls (NFP) reports, inflation data, interest rate decisions, geopolitical tensions, and trade developments.
- Asian Trading Hours
While the Asian trading session (Tokyo, Hong Kong, Singapore, etc.) is generally less active for gold trading compared to the London and New York sessions, there can still be opportunities during Asian hours, especially when there are significant market developments or news from Asia.
How to trade gold online?
Trading gold online involves several steps and considerations. Here is a general guide on how to trade gold online:
- Choose a Reliable Broker
Select a reputable online brokerage platform that offers access to gold trading. Ensure that the broker is regulated, has a user-friendly interface, provides competitive pricing, and offers a range of trading tools and resources.
- Open an Account
Sign up and open a trading account with the chosen brokerage platform. Complete the necessary registration process, provide identification documents, and verify your account as per the broker's requirements.
- Fund Your Account
Deposit funds into your trading account using a preferred payment method, such as bank transfer, credit/debit card, e-wallets, or other payment options supported by the broker.
- Research and Analysis
Before trading, conduct thorough research and analysis on the gold market. Stay updated with market news, economic indicators, geopolitical events, and technical analysis tools. Understand factors that influence gold prices and develop a trading strategy based on your analysis.
- Choose a Trading Platform
Most online brokers offer trading platforms that allow you to trade gold. Choose a platform that suits your preferences, whether it's a web-based platform, desktop software, or mobile app. Ensure the platform provides real-time price quotes, charting tools, order execution capabilities, and risk management features.
- Select Gold Instruments
Decide on the type of gold instrument you want to trade, such as physical gold (bullion, coins), gold futures contracts, gold ETFs, gold CFDs, or gold mining stocks. Each instrument has its characteristics, risk profile, and trading requirements.
- Place Trades
Use the trading platform to place buy or sell orders for gold. Specify the quantity, price, and order type (market order, limit order, stop-loss order, etc.). Monitor your trades and manage risk by setting stop-loss and take-profit levels.
- Manage Your Positions
Monitor your gold positions regularly and adjust your trading strategy as needed based on market conditions. Keep track of profits, losses, and overall portfolio performance. Consider using risk management techniques such as diversification, position sizing, and risk-reward ratios.
- Stay Informed and Educated
Continuously educate yourself about the gold market, trading strategies, and risk management techniques. Stay informed about macroeconomic trends, central bank policies, geopolitical developments, and market sentiment that can impact gold prices.
- Review and Evaluate
Periodically review your trading performance, analyze your trades, and evaluate the effectiveness of your trading strategy. Learn from both successful and unsuccessful trades to improve your skills as a gold trader.
It's important to note that trading gold online involves risks, including market volatility, leverage risks (for leveraged products like CFDs), and geopolitical uncertainties. Therefore, it's advisable to start with a demo account or trade with small amounts initially to gain experience and confidence before committing larger sums of capital.