HOW TO TRADE CURRENCY CORRELATION
What is currency correlation?
Refers to the relationship between two different currency pairs. Currency correlation involves comparing how the prices of two different currency pairs move in relation to each other over time. To effectively trade multiple currency pairs, it’s essential to grasp how their movements interrelate with each other unless you are trading a single pair.
TYPES OF CURRENCY CORRELATION
- Positive correlation- This is when currency pairs tend to move in the same direction. Example: EURUSD and GBPUSD currency pair
- Negative correlation- This is when pairs tend to move in opposite direction. Example: USDJPY and USDCHF currency pair
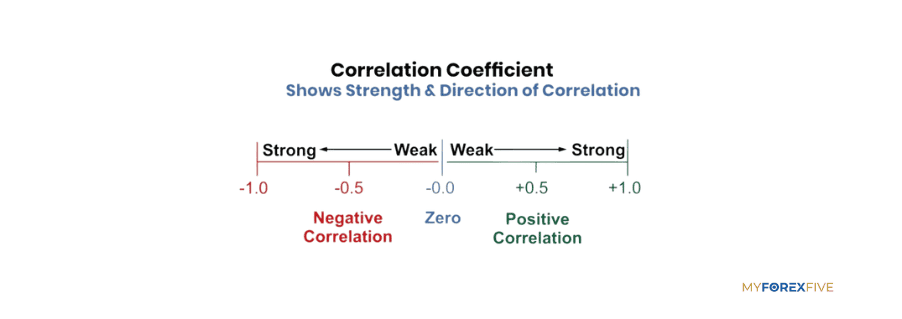
Correlation coefficient
The strength of the relationship is measured by a correlation coefficient. A coefficient of +1 means the pairs move perfectly in the same direction, -1 means they perfectly move in the opposite directions, and 0 means there’s no consistent relationship.
This means a coefficient near +1 signifies a strong positive currency correlation and the pairs will likely move in the same direction. While a coefficient near -1 signifies a strong negative currency correlation and the pairs will likely move in opposite direction.
COMMON CORRELATED CURRENCY PAIR
EURUSD and GBPUSD
These pairs often exhibit a positive correlation because both involve the US dollar as a quote currency. They tend to move in the same direction in response to economic data release and market sentiment. But also factors such as geographical proximity and sharing reserve currency status leads to simultaneous fluctuations. In the context of risk management, opening positions of both pairs is equal to doubling a position.
USDJPY and USDCHF
These pairs typically have a negative correlation with each other. When one pair strengthens (USDJPY rises), the other pair tend to weaken (USDCHF), and vice versa. This negative correlation is due to the role of the US dollar as the base currency in both pairs.
AUDUSD and NZDUSD
These pairs usually have a positive correlation because both currencies are from commodity exporting countries with similar economic structures. They often move in tandem in response to change in commodity prices and risk sentiment.
EURUSD AND USDCHF- These pairs exhibit a negative correlation, known as the ‘’Euro-Swiss’’ correlation. This relationship is due to the fact that the US dollar is the quote currency in one pair (EURUSD) and the base currency in the other (USDCHF).
How To Calculate Currency Correlation?
Below you can find a table which shows the correlation between currencies for an hour, a day, a week, a month, three months, six months and a year.
The forex currency pair correlation table shows the correlations that were calculated over a period of one month.
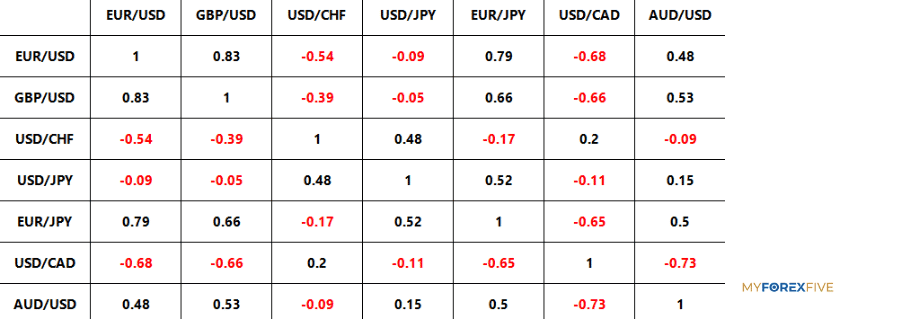
Interpretation Of The Results
let's try to understand these figures and what they mean. If the result is between:
0 – 0.2: The correlation between the pairs is insignificant; therefore, the exchange rates move randomly.
0.2 – 0.4: The correlation is not that small but is not strong either
0.4 – 0.7: There is an average correlation
0.7 – 0.9: Shows that there is a strong correlation between the pairs
0.9 – 1: Indicates that the two pairs correlate very strongly
INDEX CORRELATION
Refers to the relationship between the movements of different stock market indices. It measures the degree to which the prices of these indices move in relation to each other.
Like currency pairs, indices can exhibit:
- Positive correlation- This is when two indices move in the same direction. This suggest that they tend to rise or fall together. Example: NASDAQ and S&P 500 because both indices include many of the large-cap technology stocks, such as apple, Microsoft, and Amazon. Therefore, when the overall stock market sentiment is positive, both indices tend to rise.
- Negative correlation- This is when indices move in opposite directions. Example: Gold (XAUUSD) and USD Index (DXY)
- Neutral- When there is no clear relationship between the movement of two indices, they are said to have neutral correlation. Example: FTSE 100 (UK) and DAX (Germany)
HOW COMMODITIES CORELLATE WITH CURRENCY
One of the highest correlated currencies with commodities are the Australian Dollar, the US Dollar, the Swiss Franc, the Canadian Dollar, the Japanese Yen and the Euro.
- The Swiss Franc has a strong positive correlation with gold since 1/4th of Switzerland’s total money supply is guaranteed through gold reserves.
- Since Canada is one of the biggest net exporters of oil, it holds a strong positive correlation with the commodity.
- Japan is one of the biggest net importers of oil and hence has a strong inverse correlation with the commodity.
- As Euro is the closest alternative to the USD and the second-largest traded currency after the US dollar, it holds a positive correlation with oil and precious metals like gold.
- The Australian Dollar is strongly and positively correlated with the prices of precious metals like gold, copper and silver since Australia is one of the highest producers of these metals especially gold.
- The US dollar is inversely correlated with most commodities, especially oil since all commodities are quoted in the US dollar. Hence, when the US dollar is strong, one needs a lesser amount of the US dollars to buy the commodity and vice versa.
CURRENCY CORRELATION TRADING TIPS
- Understand how different currency pairs move in relation to each other. Positive correlation means pairs move in the same direction, while negative correlation indicate opposite movements.
- Use correlation coefficients to quantify the strength of the relationship between pairs. Correlation values range from -1 to +1, with closer to +1 indicating a stronger positive correlation and closer to -1 indicating a stronger negative correlation.
- If you want to diversify trades look for pairs with correlated figure between -0.3 to +0.3 as that suggest they are not correlated, this can reduce risk exposure.
- Combine correlation analysis with technical analysis to identify potential trading opportunities.
- Keep track of economic indicators and events that can influence currency movements. Look for factors such as interest rate decisions, economic data release, and geopolitical events that can impact correlation dynamics.
- Implement proper risk management techniques, such as setting stop-loss orders and position sizing, to protect your capital in case correlation break down unexpectedly.
Conclusion
Currency pairs correlation is usually the thing that everybody has heard about before but few traders really knows how to use it properly. If you want to succeed and thrive in this hectic environment, and eventually make a profit, you need to know the existence of it.